Aldweib及同事评价既往血运重建的无症状患者心肌灌注成像和后续血运重建的益处。6750例既往血运重建患者接受心肌灌注闪烁显像(MPS),769例有缺血且无症状,15%进行血运重建。接受血运重建治疗与接受药物治疗的缺血患者相比,全因死亡无差异。在校正基线特征、既往血运重建类型、MPS数据和倾向评分后,只有年龄和高胆固醇血症,而非血运重建,与死亡率相关。既往血运重建且MPS提示,可诱导缺血的无症状患者未从再次血运重建中获得生存获益(图3)。
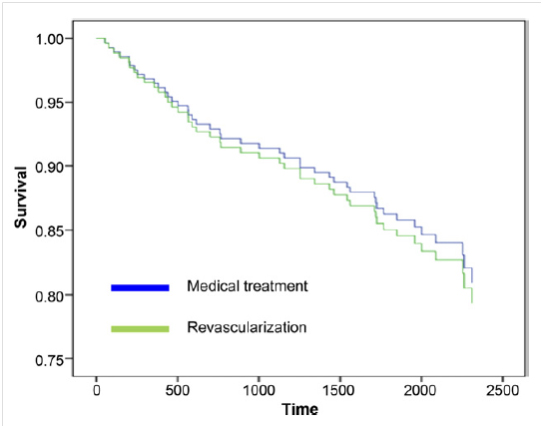
图3. 校正年龄、性别、射血分数的倾向配对患者生存率
J Am Coll Cardiol.2013;61(15):1616-1623.
特约点评
血运重建后无症状患者常规负荷核素显像及随后的血运重建
Routine Nuclear Stress Testing and Subsequent Revascularization in Asymptomatic Patients Following Coronary Revascularization
Zaher Fanari, Sandra Weiss, William S Weintraub.
Christiana Care Health System, Newark, DE,美国
Myocardial perfusion scintigraphy (MPS) can stratify risk in symptomatic and asymptomatic patient. However, the benefit of such testing to guide subsequent revascularization in patients with stable coronary disease and asymptomatic patients is uncertain. Moreover, MPS testing in patients’ post-revascularization remains widely utilized, justified by the assumption that post-revascularization ischemia is an adverse prognostic finding regardless of symptoms, and that repeat revascularization would be of benefit in reducing subsequent events, in particular myocardial infarction (MI) or death. However, there is little evidence supporting such a practice. In the April issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, Aldweib et al. compared the survival of asymptomatic patients with MPS-identified post-revascularization ischemia who subsequently underwent repeat revascularization in addition to optimal medical therapy (OMT) versus OMT alone. The authors performed a retrospective analysis of 769 patients, in whom 115 (15%) underwent repeated revascularization in response to identified ischemia. The study demonstrated no difference in the primary endpoint of all-cause mortality between the revascularization and OMT groups (18.3% vs. 19.1%, P=0.84), despite adjustment for degree of MPS ischemia (mild vs. moderate-severe), degree of scar, and left ventricular ejection fraction using propensity score methods. The authors concluded that routine MPS and subsequent intervention in patients with post-revascularization silent ischemia did not offer survival benefit.
This study should be praised in that it is the first to evaluate post-revascularization patients with silent ischemia by MPS, a population that heretofore has not been studied and where questions regarding management certainly remain. This lack of data on reflexive stress imaging post-revascularization is highlighted by the disparity in current practice guidelines and appropriateness statements on this issue. Notably, the 2011 Guidelines on Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) recommends against routine testing, while the 2009 Appropriate Use Criteria for Cardiac Radionuclide Imaging suggests that stress testing 2 years following PCI and less than 5 years following CABG is considered uncertain, leaving room for individual interpretation of appropriateness in patient who remain asymptomatic. Although revascularization of identified ischemia in increasingly symptomatic, medically optimized patient is well established and appropriate, further intervention on previously revascularized individuals with residual silent ischemia is based largely on extrapolation from studies performed in patients with chronic stable angina or asymptomatic, but previously unrevascularized individuals. These patient populations are quite unique from that which was studied here and whose study findings were inconsistent.



 京公网安备 11010502033353号
京公网安备 11010502033353号